Tools and Demos
I have developed a tool for explanation in inconsistent knowledge bases called DALEK and built an ontological knowledge base for Durum Wheat sustainability. This was done during my thesis with the funding of the ANR DUR-DUR project.
DiALectical Explanation in Knowledge-based systems (DALEK)
Abdallah Arioua, Madalina Croitoru and Patrice Buche, University of Montpellier, LIRMM GraphIK/IATE AXE 5, France.
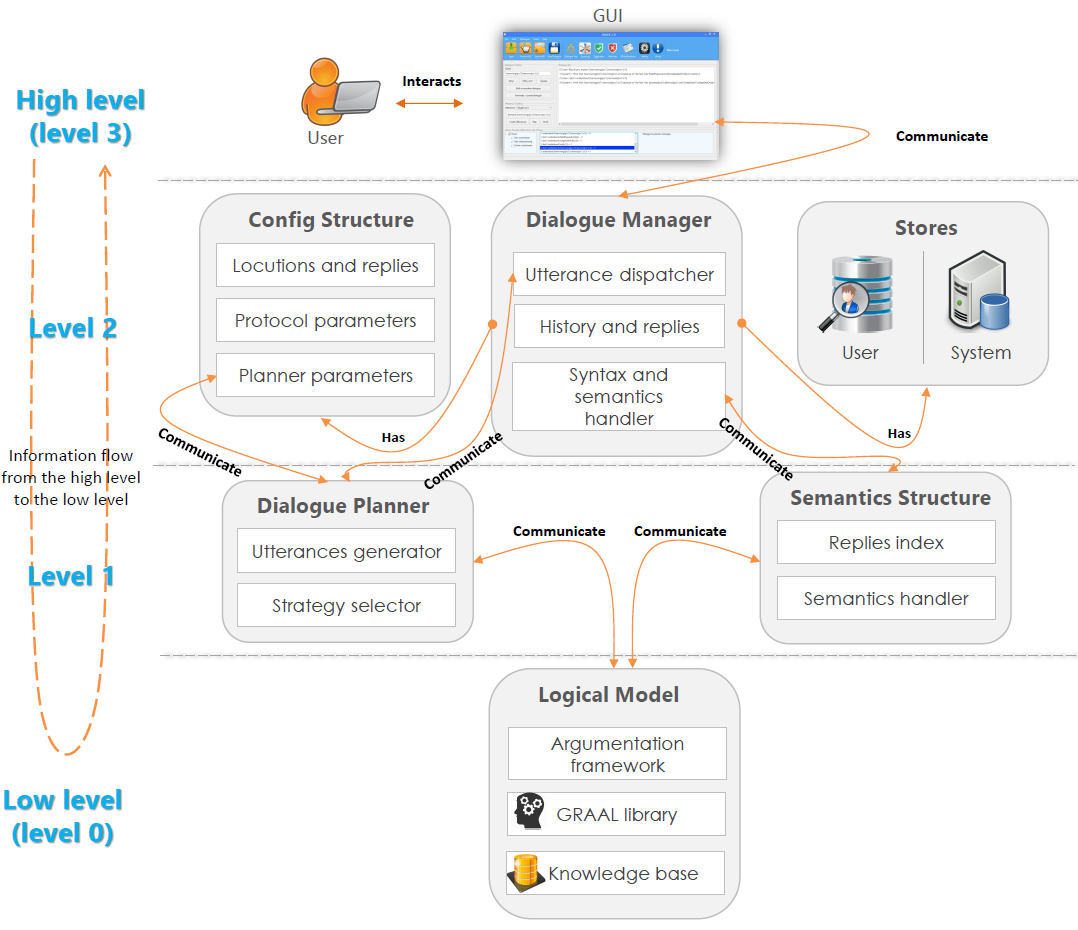
In this section we explain the DALEK (DiALectical Explanation in Knowledge-based systems) framework for explanation and argumentation in inconsistent knowledge bases. The user can start a pure explanation dialogue where argumentation is not included or a dialogue of pure argumentation, or both. Besides this local generality, DALEK is programmed in a way that it captures a standalone argumentation dialogue like the well-known model of Prakken (2006) and stand alone explanatory dialogues of Walton. DALEK engages a User (or an Expert) and the Reasoner in a dialogue about the entailment of any query in potentially inconsistent Datalog+/- knowledge bases. The layered architecture is shown in the figure bellow and it is detailed as follows:- Level 3 (high level): the graphical user interface.
- Level 2: dialogue manager, confguration structure and stores.
- Level 1: dialogue planner and semantics structure.
- Level 0 (low level): logical model.
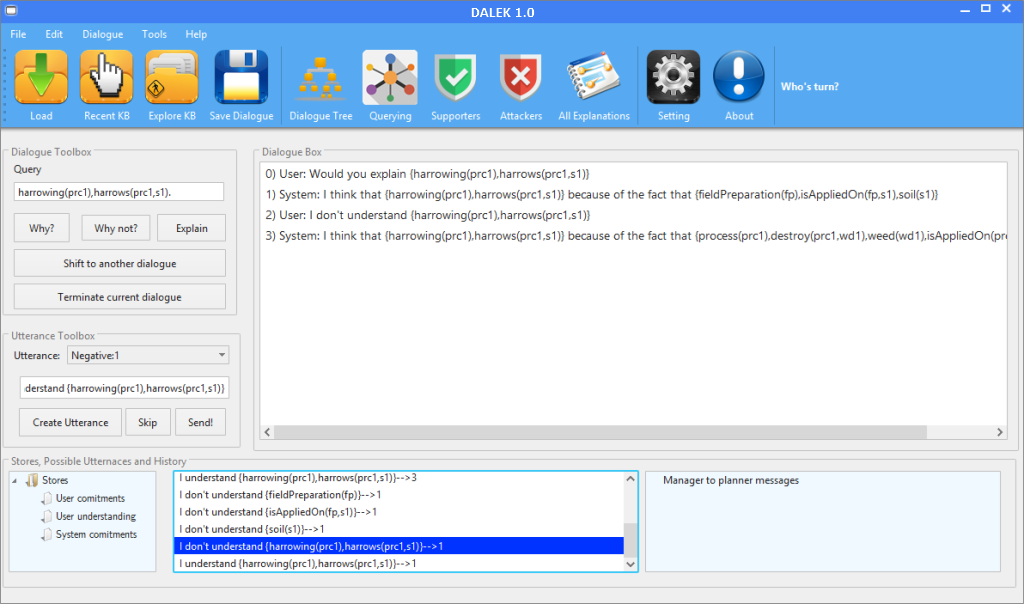
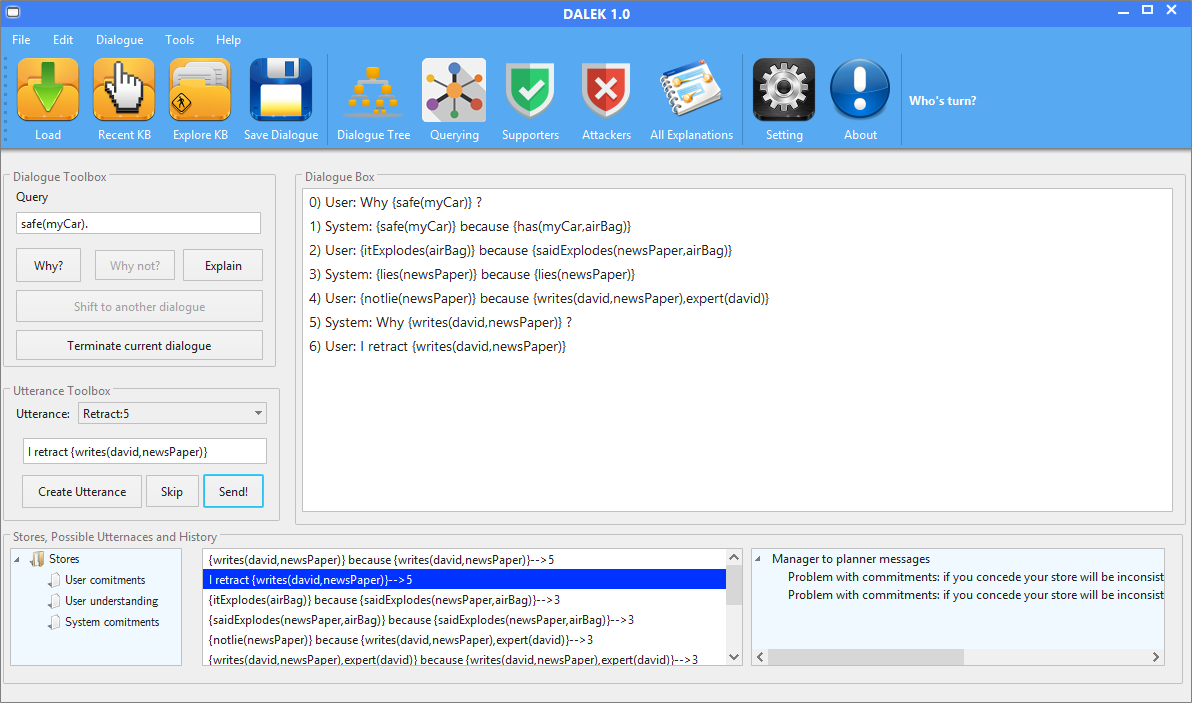
Demo
Please find here the Demo presented in COMMA 2016 about DALEK. The paper is entitled "DALEK: a Tool for Dialectical Explanations in Inconsistent Knowledge Bases".
Publications:
- Explanatory Dialogues with Argumentative Faculties over Inconsistent Knowledge Bases. Arioua, A.; Croitoru, M.; and Buche, P. International Journal of Expert Systems With Applications, 2017.
- DALEK: a Tool for Dialectical Explanations in Inconsistent Knowledge Bases. Arioua, A.; and Croitoru, M. In Proceedings of the the 6th International Conference on Computational Models of Argument, COMMA 2016, pages 461--462, 2016.
The Durum Wheat Knowledge Base 0.1
Abdallah Arioua, Madalina Croitoru, Patrice Buche and Rallou Thomopoulos, University of Montpellier, LIRMM GraphIK/IATE AXE 5, France.
This web site is the official webpage for the durum wheat knowledge base. It contains downloadable materials alongside with descriptions of the different components of the knowledge base.
- Author : Abdallah Arioua, Patrice Buche, Madalina Croitoru and Rallou Thomopoulos
- Contact : arioua@supagro.inra.fr, abdallaharioua@gmail.com
- Institute : UMER IATE, LIRMM/graphik, University Montpellier, Montpellier - France
- Last update : 28/09/2015
ANR DUR-DUR project
The durum wheat knowledge base was constructed within the French National Project (ANR) DUR-DUR (ANR-13-ALID-0002). The goal of this knowledge base, among others,
is to integrate a part of the scientific knowledge acquired during the project to redesign the durum wheat chain.
The Dur-Dur project suggests developing a systematic approach to investigate issues related to the management of the nitrogen, energy and contaminants, to guarantee a global quality of
products throughout the production and the processing chain. Started in 2014 and planned over 4 years, this multi-factorial approach aims at integrating the 3 dimensions of the
sustainability (environmental, economic, and social), at 4 levels of investigation. A task of integration by multi-criteria analyses
and knowledge engineering aims at identifying the efficient levers to improve and guarantee the sustainability of the durum wheat agri-food
chain (task 5).
This knowledge base is the fruit of the integration task. It will be used in many computational tasks, notably analysing and comparing the alternative innovative technical itineraries proposed in the project to reduce the dependence to chemical inputs (nitrogen fertilizers and pesticides).
Description
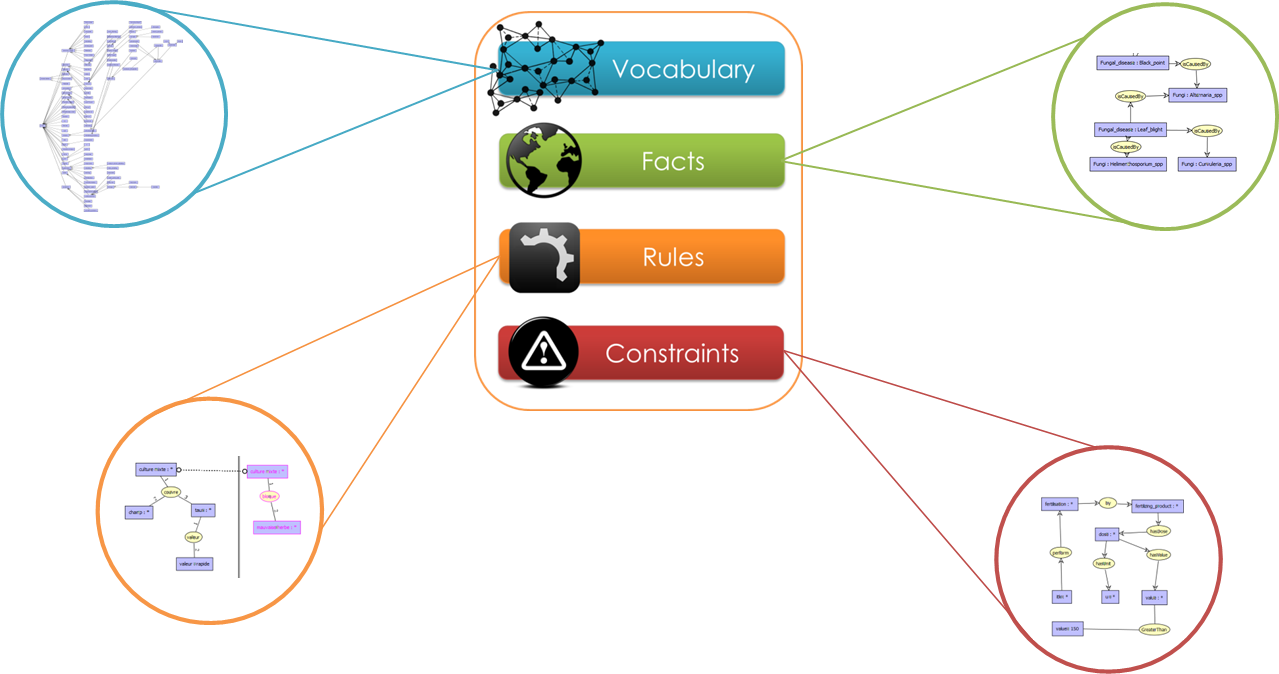
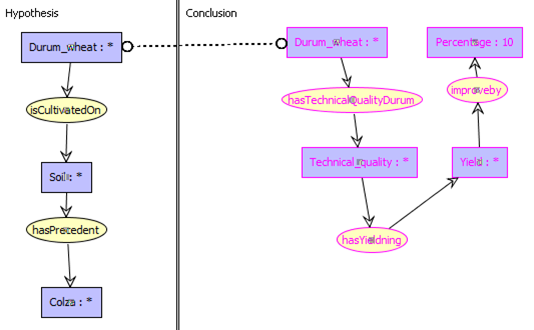
The knowledge base represents domain-specific knowledge, e.g. agronomy. It is composed of four main parts: the vocabulary, facts, rules and negative constraints. It is represented within the framework of existential rules (Datalog+/-). The vocabulary contains 533 concepts and 200 relations. The rule-base contains 30 rules (including existential rules and excluding concept and relation types hierarchy rules) and 22 n-ary negative constrains (excluding banned type constraints). The factual part has about 865 atoms. atoms.
The knowledge base is authored by CoGui 1.6b which is a graph-based authoring tool (small circles depict it). The syntax and the consistency of the facts is validate by means of CoGui engine and exported to an RDF/XML format whereas the vocabulary, rules and negative constraints are exported as DLGP format 2.0 (Data LoG Plus). It is worth noticing that some parts of the vocabulary has been built upon Agropedia indica.
In what follows we present the different components and some snapshots on the content of each component:
The structure detailed
In what follows we give a more detailed view on the structure of the knowledge base where we mention the consistent and inconsistent cases of our knowledge base.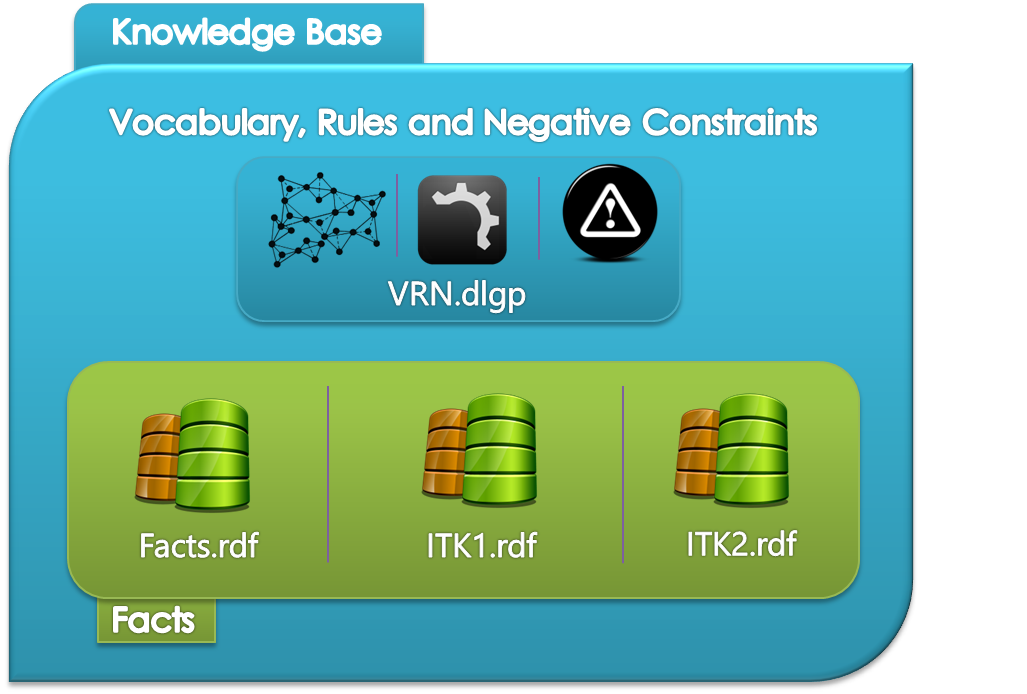
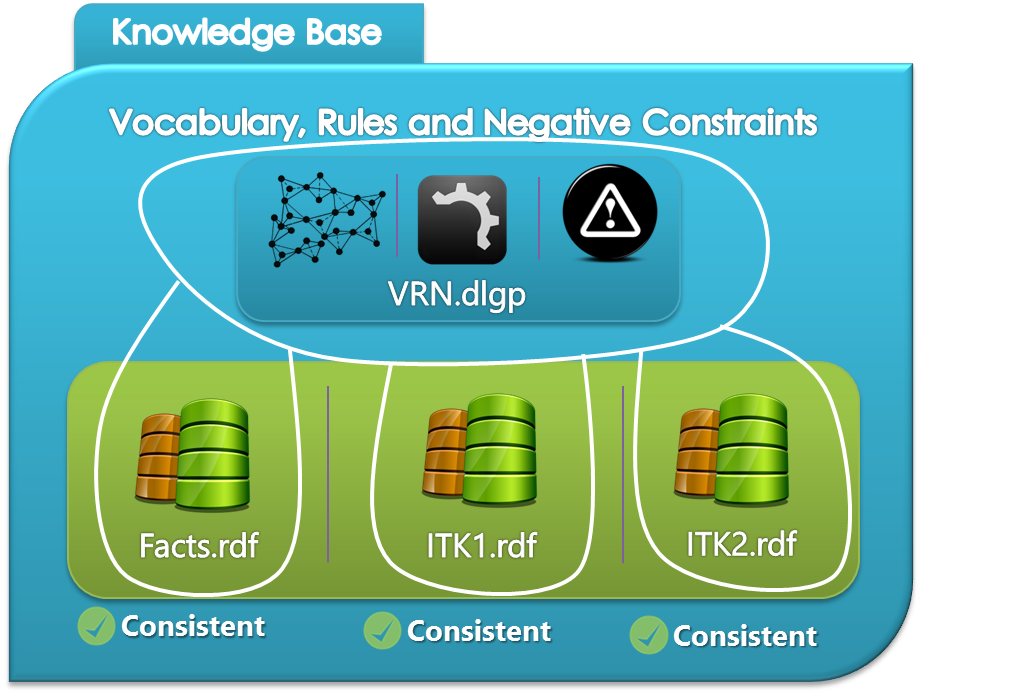
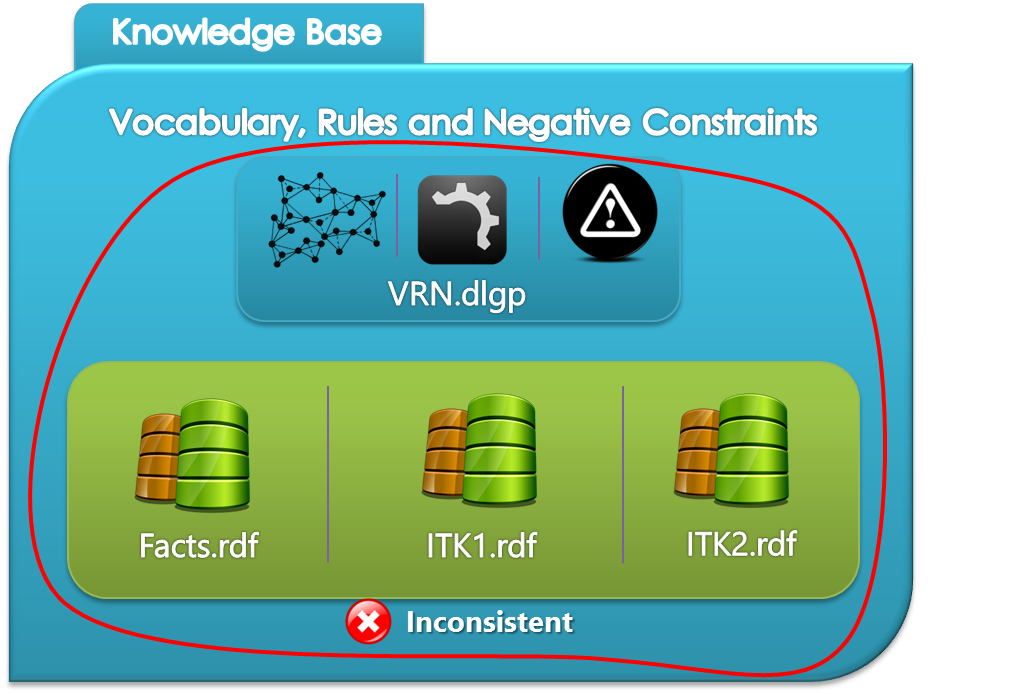
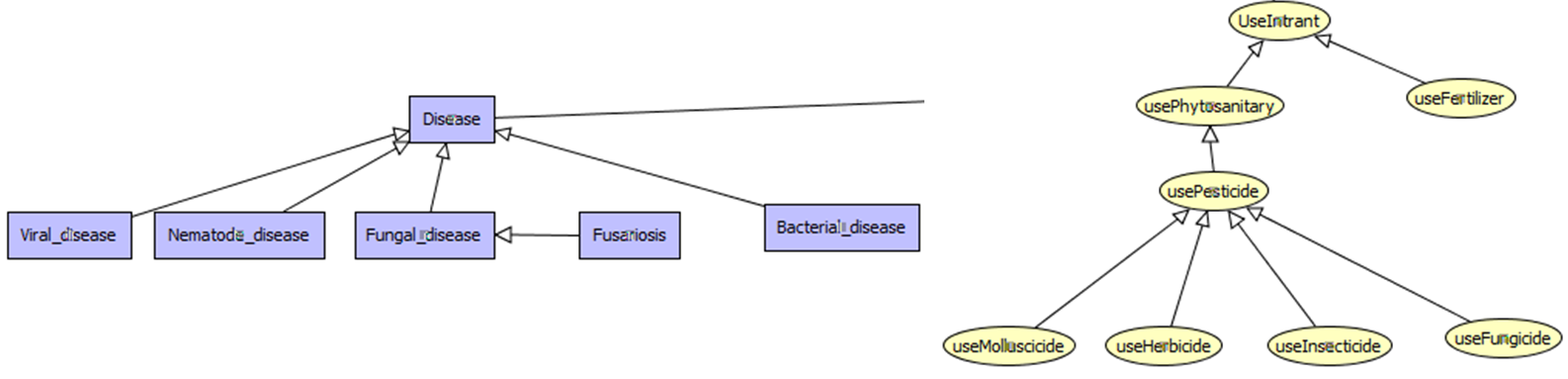
Snapshots
Cite the follwing article if you use the knowledge base.
Publications:
- A Datalog±± Domain-Specific Durum Wheat Knowledge Base. Arioua, A.; Buche, P.; and Croitoru, M. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Metadata and Semantics Research, MTSR 2016, pages 132--143, 2016. . @inproceedings{AriouaBC16, author = {Abdallah Arioua and Patrice Buche and Madalina Croitoru}, title = {A Datalog{\(\pm\)} Domain-Specific Durum Wheat Knowledge Base}, booktitle = {Metadata and Semantics Research - 10th International Conference, {MTSR} 2016, G{\"{o}}ttingen, Germany, November 22-25, 2016, Proceedings}, pages = {132--143}, year = {2016} }